On February 9, or the last day of the Year of the Cat, doctors of the Central Lung Hospital performed a double lung transplant on a 21-year-old patient. This is the most difficult among the organ transplant techniques.
    |
 |
|
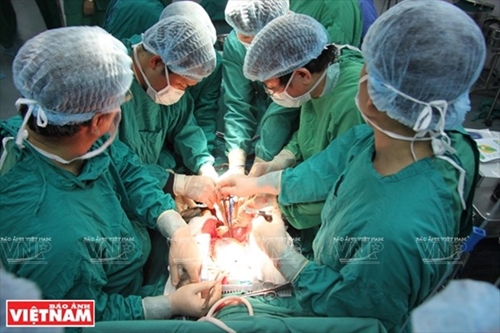
Doctors at Military Hospital 103 perform an organ transplant. Photo: VNP |
The transplant was successful at the highest level according to international standards from the UCSF Lung Health Center - one of the nine largest and most prestigious lung transplant centers in the U.S., showing that Vietnam has approached and mastered the top technique in the field of organ transplant.
At the Asian Transplantation Week 2023 (ATW 2023), the organizing committee designed a seminar on the Vietnamese organ transplant industry, and this proves the country's position and reputation in the specialized and complex technique.
The result is thanks to efforts of Vietnamese doctors and scientists over the past 30 years since the first kidney transplant for a 40-year-old patient with terminal-stage kidney failure conducted in 1992 at Military Hospital 103.
In 2017, Vietnam successfully performed the first lung transplant and heart transplant for a pediatric patient. A year later, the country carried out lung and kidney transplants from brain-dead donors with success. In 2019, a series of surgeries to transplant multiple organs from brain-dead donors were performed simultaneously. In 2020, the first limb transplant surgery in Southeast Asia and intestinal transplant from a living donor were successfully performed, helping Vietnam become one of the 22 countries in the world that can perform intestinal transplant techniques. In 2023, heart and kidney transplants were conducted with the coordination of hospitals in Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi.
Currently, Vietnam has 25 organ transplant centers across the country, not only at the central level but also at the local one. By the beginning of 2024, there had been nearly 8,000 organ transplants performed, including more than 7,000 kidney transplants and 500 liver transplants, meaning that many lives have been extended.
Vietnam has now mastered the most important and common organ transplant techniques in clinical practice, such as kidney, heart, liver, pancreas, and lung, with an even higher survival rate after organ transplants than in developed countries. Particularly, the cost of organ transplants in Vietnam is only about 1/8 of that in Thailand and 1/24 of that in the U.S.
However, experts held that the biggest difficulty currently facing the Vietnamese organ transplant industry is the lack of organ tissue sources for transplant while the demand is high.
According to the Ministry of Health, the number of organ transplant cases in Vietnam has increased significantly from 283 in 2014 to 1,004 in 2022. There are more than 5,000 cases on the national organ transplant waiting list.
In recent years, the number of people registering to donate organs has increased significantly, from 265 in 2014 to more than 73,000 by the end of June 2023. However, this is still modest compared to the demand.
Vietnam has applied the Law on Donation, Removal and Transplant of Human Tissues and Organs and Donation and Recovery of Cadavers, along with many legal documents in the fields of donation, regulation and transplant of tissues and organs. Meanwhile, the Health Insurance Law allows insurance payments for examination and organ transplant costs as well as post-transplant treatment.
Currently, the country has 23 hospitals recognized by the Ministry of Health as qualified to perform organ retrieval and transplantation techniques. In addition, the ministry has also licensed the operation of 10 tissue banks.
Experts recommended that Vietnam should promptly deal with shortcomings in policies and legal regulations in the field, while forming a network of consultants to encourage organ donation after death or brain death, and strengthening communications to provide the mass with better understanding of organ donation and great significance of this noble act.
Source: VNA